[Guide] The wide application and development of electronic devices will inevitably lead to the continuous increase of the level of electromagnetic fields they generate in the surrounding space. In other words, electronic equipment inevitably works in the electromagnetic environment (EME). Therefore, the adaptability of electronic equipment in the electromagnetic environment must be solved. Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) is a science about the resistance to electromagnetic interference (EMI). Key words: EMEEMCEMI electromagnetic compatibility With the rapid development of electronic technology, modern electronic equipment has been widely used in various fields of human life. At present, electronic equipment is in a period of rapid development, and this development process is still continuing at an increasing rate. The wide application and development of electronic equipment will inevitably lead to the continuous increase of the level of electromagnetic fields they generate in the surrounding space. In other words, electronic equipment inevitably works in the electromagnetic environment (EME). Therefore, the adaptability of electronic equipment in the electromagnetic environment must be solved. Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) is a science about the resistance to electromagnetic interference (EMI). Classification of electromagnetic interference sources Various forms of electromagnetic interference are the main factors that affect the electromagnetic compatibility of electronic equipment. Therefore, it is an important content to be studied in the design of electromagnetic compatibility. The sources of electromagnetic interference can be divided into internal interference and external interference. Internal interference refers to the mutual interference between the various components inside the electronic equipment, including the interference caused by the leakage of the working power through the distributed capacitance and insulation resistance of the line (related to the working frequency); the impedance of the signal through the ground wire, power supply and transmission wire Mutual coupling, or interference caused by mutual inductance between wires; some components inside the device or system generate heat, which affects the stability of the component itself or other components; interference caused by high-power and high-voltage components affects other fields through coupling Interference caused by components. External interference refers to the interference of factors other than electronic equipment or system on the circuit, equipment or system, including external high voltage, power supply interferes with the electronic circuit, equipment or system through insulation leakage; external high-power equipment generates strong space Magnetic field interferes with electronic circuits, equipment or systems through mutual inductance coupling; space electromagnetic waves interfere with electronic circuits or systems; unstable working environment temperature causes interference caused by changes in internal circuit parameters of electronic circuits, equipment or systems; powered by industrial power grids Equipment and interference caused by the grid voltage through the power transformer. Dissemination of interference When the frequency of the interference source is higher, the wavelength of the interference signal is smaller than the structure size of the interfered object, or the distance between the interference source and the victim r》》 λ / 2π, the interference signal can be regarded as a radiated field, It emits electromagnetic field energy in the form of plane electromagnetic waves and enters the path of the interfered object. The interference signal is in the form of leakage and coupling, through an insulating support, etc. (including air) as a medium, and enters the interfered line, equipment or system through the coupling of the common impedance. If the frequency of the interference source is low, the wavelength λ of the interference signal is longer than the structure size of the interfered object, or the distance between the interference source and the interfered object r << λ / 2π, then the interference source can be considered as a stable field, it The path into the interfered object in the form of an induction field. Interfering signals can be introduced into lines, equipment or systems through direct conduction. Basic principles of electromagnetic compatibility design The first is grounding. The purpose of grounding includes: ensuring that the circuit system can work stably; preventing interference from external electromagnetic fields; and ensuring safe operation. The second is shielding. Shielding is to isolate the metal between two space areas to control the induction and radiation of electric fields, magnetic fields and electromagnetic waves from one area to another. The principle of shield material selection is: when the frequency of the interference electromagnetic field is high, use a metal material with low resistivity; when the frequency of the interference electromagnetic wave is low, use a material with high permeability; in some occasions, if required When it has good shielding effect on high-frequency and low-frequency electromagnetic fields, different metal materials are often used to form a multi-layer shield. In addition, there are other methods to suppress interference, including filtering, the correct selection of passive components and circuit technology. Filtering is an important measure to suppress and prevent interference. The filter can significantly reduce the level of conducted interference. For high-frequency circuits, a CLCMπ filter composed of two capacitors and an inductor (high-frequency choke) can be used. There are many types of filters, and choosing an appropriate filter can eliminate undesirable coupling. Practical passive components are not "ideal", their characteristics are different from ideal characteristics. Practical components may themselves be a source of interference, so it is very important to choose passive components correctly. Sometimes you can use the characteristics of components to suppress and prevent interference. Sometimes after shielding is still unable to meet the requirements of suppression and interference prevention, you can combine shielding, take balance measures and other circuit technologies. Balanced circuit means that the two wires in a two-wire circuit and all circuits connected to these two wires have the same impedance to ground or to other wires. Specifications and standards for electromagnetic compatibility issues The Special Interference Committee (CISPR) focuses on the measurement of interference noise in radio systems. In 1976, CISPR began to formulate EMI standards for electromagnetic interference. In October 1900, the republished standards were published on the basis of several revisions. Subsequently, the committee also reviewed with the International Wireless Communications Advisory Committee to formulate data requirements and specific methods for the electromagnetic compatibility testing of electronic products. Developed the "Permitted Values ​​and Measurement Methods of Interference Characteristics of Radio Instruments for Industrial, Scientific and Medical Use" (Standard No. 11) that targets the noise of information technology devices: "Measurement methods and allowable values" (Standard No. 12): "Measurement methods and allowable values ​​of radio interference characteristics of radio and television receivers" (Standard No. 13), etc. It was not until mid-1992 that the international EMI standards were finally perfected. The tolerances recommended by CISPR have been adopted by many countries in the world and serve as the basis for their national regulations. Solving some typical electromagnetic compatibility problems Due to the wide application of electronic technology in all walks of life, electromagnetic waves are everywhere in the space of human activities. Therefore, electronic equipment cannot work compatiblely without solving the problem of electromagnetic wave interference. In practical applications, people have accumulated a lot of experience in researching anti-jamming technology, and have constantly developed many practical methods to eliminate electromagnetic interference. The software anti-interference of microcomputer equipment is mainly to stabilize the memory data and ensure the program pointer. The microcomputer is a programmable control device, and the software can support and strengthen the anti-interference ability of the hardware. Ensuring the electromagnetic compatibility of the equipment is a complex technical task, and there is no universal solution to this problem. Electromagnetic compatibility technology covers a wide range, and the field of electromagnetic compatibility is also developing. It is important to master the basic principles of electromagnetic compatibility, and carefully analyze and test to choose the appropriate solution to the problem.
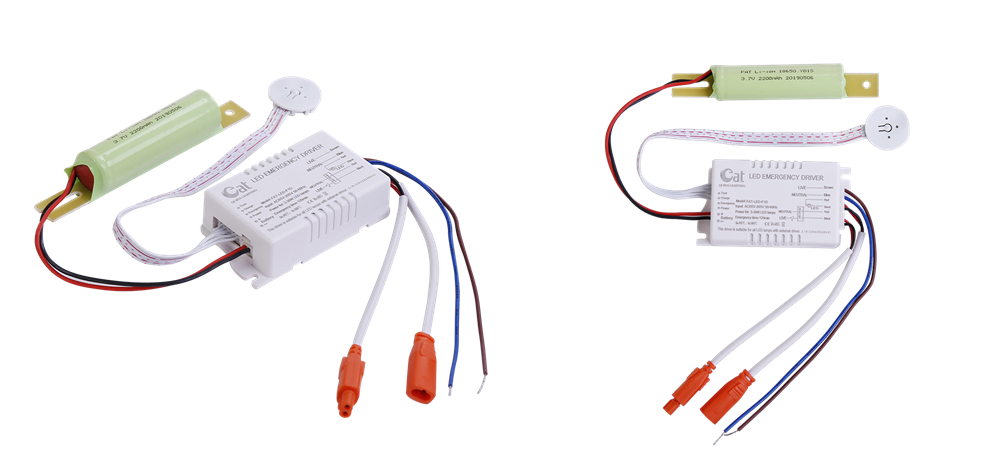
The Led Emergency Inverter is a combination of a white high-quality ABS shell and an external lithium ion battery , which is small in size and easier to hide in the ceiling . This Emergency Conversion Kit is suitable for all external driver of LED lights in the wide voltage AC85-265V range , equipped with lithium ion battery that can be recharged up to 500 times , the emergency power supply has multiple protection functions , such as overcharge , over-discharge , short circuit protection , etc .
Led Inverter,Led Power Converter,Led Emergency Battery Driver,Emergency Light Conversion Kit Jiangmen City Pengjiang District Qihui Lighting Electrical Appliances Co., Ltd , https://www.qihuilights.com