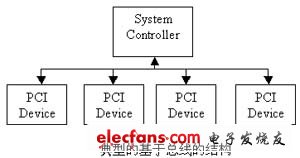
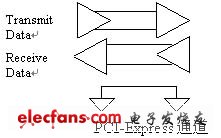
This content introduces the knowledge of PCI bus/PCI-X interface and PCI-PCI-Express, and explains the connection from PCI, PCI-X to PCI-Express. The PCI bus is a local bus that does not depend on a specific processor. From the structural point of view, PCI is a first-level bus inserted between the CPU and the original system bus. The specific management of this layer is realized by a bridge circuit, and the interface between the upper and lower sides is realized to coordinate the data transmission. The manager provides signal buffering to support 10 peripherals and maintain high performance at high clock frequencies. The PCI bus also supports bus mastering technology, allowing smart devices to take control of the bus when needed to speed up data transfer. The PCI bus system requires a PCI control card that must be installed in a PCI slot. This type of slot is currently the largest number of slots on the motherboard. On current popular desktop boards, ATX-based motherboards typically have 5 to 6 PCI slots, while smaller MATX motherboards come with 2~3 PCI slots. Depending on the implementation, the PCI controller can exchange 32-bit or 64-bit data with the CPU at a time, which allows the intelligent PCI auxiliary adapter to perform tasks in parallel with the CPU using a bus mastering technique. PCI allows multiplexing techniques that allow more than one electronic signal to exist simultaneously on the bus. In the current architecture, peripherals (network, storage, and video) are connected using parallel buses like PCI or PCI-X. Parallel buses have evolved from 32-bit 33 megabits of PCI to 64-bit 133 megabytes of PCI-X. As the clock rates of parallel buses increase, the number of slots supported by these buses decreases. Parallel buses typically contain address/data signals and some sideband signals. The sideband signal is used to indicate the direction of the data on the bus and the type of transaction, and can also be used to indicate an interrupt or bus master request. A typical 64-bit PCI-X bus can contain 64 address/data lines and 33 left and right sideband signals in a total of 127 signal pins. PCI-X interface The PCI-X interface is an updated version of the parallel PCI Express (Peripheral CompONents Interconnect) that still uses traditional bus technology, but with a larger number of wiring pins, and all connected devices as described above share all available The bandwidth. The difference from the original PCI interface is that the PCI-X uses 64-bit width to transmit data, so the bandwidth is automatically doubled, and the length of the expansion slot is inevitably increased. In addition, the rest of the connector formats including the transmission protocol, signal and standard are compatible. The advantage is that the 3.3-volt 32-bit PCI adapter can be used in the PCI-X expansion slot. Of course, if you wish, The 64-bit PCI-X adapter card can be connected to a 32-bit PCI expansion slot, but the bandwidth speed will be greatly reduced. As the bandwidth requirements for networking, storage and video have grown, some designers are looking at point-to-point structures as potential solutions. In a bus-based architecture, bandwidth is shared by all devices in the bus. In a PCI-Express point-to-point architecture, each device has a dedicated connection and does not have to share bandwidth. The point-to-point structure has other advantages. A typical PCI-Express connection uses two LVDS (low voltage differential signaling) pairs, one for transmission and one for reception. There are no sideband signals in this structure. The figure below shows a point-to-point channel with two differential pairs (one for one receive) and one ground signal. A PCI-Express channel transmits data at 2.5 Gb/s in both directions and uses 8b/10b encoding. PCI Express The PCI Express interface varies depending on the bus width, including X1, X4, X8, and X16 (X2 mode will be used for the internal interface instead of the slot mode). Shorter PCI Express cards can be inserted into longer PCI Express slots for use. The PCI Express interface is capable of supporting hot plugging, which is also a big leap. The PCI Express card supports three voltages of +3.3V, 3.3Vaux, and +12V. The PCI Express interface used to replace the AGP interface has a bit width of X16, which will provide 5GB/s of bandwidth, even with loss of coding. It still provides around 4GB/s of actual bandwidth, far exceeding the AGP 8X's 2.1GB/s bandwidth.
New Wholesale OEM music noise cancelling Wireless Bluetooth Headphones with Mic
1: Function:Bluetooth with Microphone, active noise cancelling reduction
2: Feature: rubbish finish with High quality ( 1 pcs of bluetooth headphone, 1 charging cable)
3:Use for :PC / mobile Phone /listening music and suit for all video Bluetooth device
Items as below:
Noise Cancelling Bluetooth Headphones Noise Cancelling Bluetooth Headphones,Noise Cancelling Headphones With Microphone,Noise Cancelling Headphones,Wireless Noise Cancelling Headphones Shenzhen Greater Industry Co., Ltd. , https://www.szgreater.net