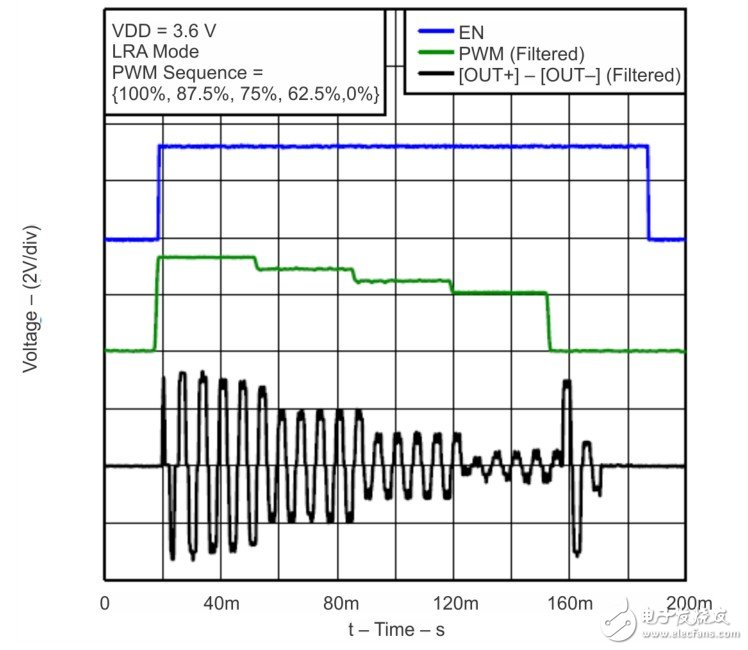
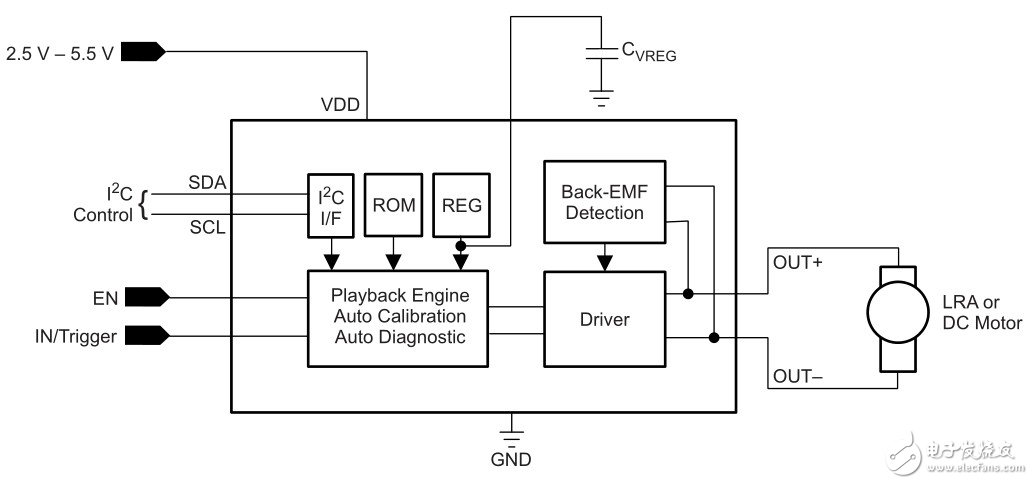
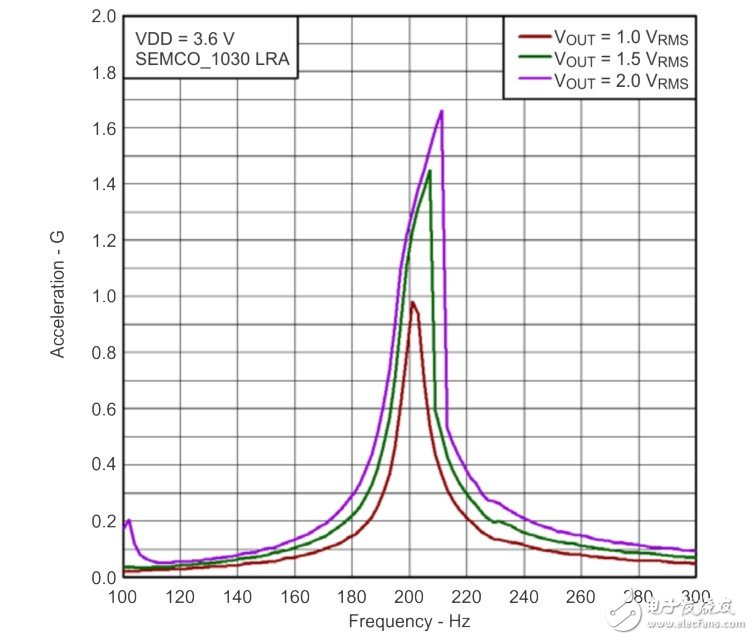
Author: Texas Instruments (TI) company HapTIc product line Brian Burk 1 Introduction DRV2605 is a haptic driver for off-axis moment of inertia (ERM) and linear resonance actuator (LRA) (with built-in library and intelligent control Eng). The DRV260x series devices use a special LRA control algorithm called automatic resonance tracking. Automatic resonance tracking uses the back-EMF of the LRA to detect and track the resonance frequency. Later, it can use this resonance frequency information to drive a closed-loop LRA. Auto-resonance has many benefits and makes LRA integration simple: • The actuator vibration is stronger and more consistent • Lower power consumption of resonance drive • With over-speed driving and LRA braking capabilities, get better response time Figure 1 shows the input and output signals of an automatic resonance tracking system. Figure 1 LRA automatic resonance detection The green waveform is the (PWM) input of DRV2605. It is a filtered PWM modulated DC signal that represents the waveform envelope and amplitude of the output waveform. The black line is the sine wave output generated by DRV2605 which detects the resonance frequency. 2 Principle of automatic resonance tracking Automatic resonance tracking uses the back EMF generated by the LRA to detect the resonance frequency. TI described this back-EMF to determine the best way to control LRA frequency, vibration intensity, and start / stop time. Figure 2 DRV2605 structure diagram Automatic resonance tracking utilizes the electromechanical properties of LRA. Inside the LRA, as the magnet approaches or moves away from the drive electrode, the back EMF will change accordingly. Each cycle, DRV2605 will detect this back-EMF signal at the output pin and send it to the auto-resonance engine. After that, the auto resonance engine determines its frequency. If the frequency is too high, DRV2605 will reduce the output frequency; if the frequency is too low, DRV2605 will increase the output frequency. This dynamic tracking ensures more consistent vibration. If a non-automatic resonant driver is used, it is difficult to achieve consistent vibration because the LRA resonant frequency will always vary with manufacturing tolerances and environmental factors. Tracking the resonance frequency in real time is important to maintain the strength and consistency of the vibration. 3 Automatic resonance vibration intensity The resonant frequency of the linear resonant actuator is very narrow, as shown in Figure 3. This narrow resonance frequency is caused by the resonance performance of the LRA internal spring and the mass. At a certain frequency, the resonance frequency of one end of the LRA will drop sharply. Figure 3 Resonant frequency of linear resonant actuator Figure 3 shows the relationship between acceleration and frequency using the output voltage of three different drivers. As the voltage increases, as with acceleration, the resonance frequency also changes, which prevents us from determining the LRA's resonance frequency in advance. Xinxiang Mina Import & Export Co., Ltd. , https://www.mina-motor.cn