Wash Lights Moving Head,Wash Mini Led Moving Head,Moving Head Wash Light,Beam Spot Wash Moving Head Guangzhou Cheng Wen Photoelectric Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.cwledwall.com
A simple production process of led energy-saving lamps
**The Simple Production Process of LED Energy-Saving Lamps**
LEDs, also known as light-emitting diodes, are semiconductor devices made from compounds like gallium (Ga), arsenic (As), and phosphorus (P). Today, LEDs and their corresponding driver circuits are widely used in energy-saving street lights, office lighting, and electronic products. They have become a popular choice due to their high brightness, low power consumption, long lifespan, and environmental benefits. LED energy-saving lamps use high-brightness white LEDs, which are considered the ideal cold light source for the future, especially for home lighting.
Compared to traditional incandescent and fluorescent lamps, LED energy-saving lamps offer significant advantages. The luminous efficiency of LEDs exceeds 90%, while incandescent bulbs only reach around 20% and fluorescent lamps about 40%. This makes LED lamps highly efficient and energy-saving. Additionally, LEDs operate on direct current, providing a steady light without flickering, which is easier on the eyes and reduces eye strain.
Another major benefit of LED lamps is that they do not contain harmful substances, making them easy to recycle and environmentally friendly. Unlike fluorescent lamps, which emit ultraviolet and infrared rays, LED lamps produce pure light with no radiation or heat generation. This makes them safer and more efficient in terms of energy usage.
**How LED Energy-Saving Lamps Work**
Figure 1 shows a schematic of the power supply circuit for 38 LED lamps. The lamp is powered by a 220V AC supply. First, the voltage is stepped down using resistor R1 and capacitor C1, then rectified through a full-bridge rectifier consisting of D1 to D4. Resistor R2 provides a constant current to the 38 LEDs connected in series. Each LED has a rated current of 20mA and consumes approximately 2W of power. Since LEDs tend to generate heat when concentrated, the current must be carefully controlled during design to avoid overheating.
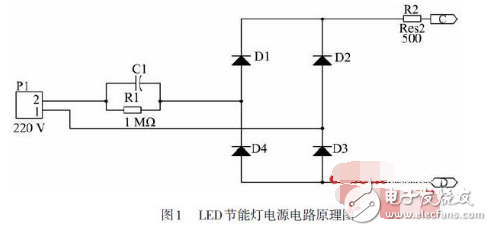
In this circuit, R1 acts as a protection resistor, while R2 limits the current to prevent voltage spikes and temperature rise. This design is ideal for small lamps, offering compact size, low power consumption, and cost-effectiveness. It’s recommended to use a polyester capacitor with a voltage rating of 400V or higher for C1, and a 1/4W resistor for R2.
**Component Parameters**
- C1: 474μF, 400V polyester capacitor
- R1: 1MΩ five-band resistor
- D1–D4: IN4007 rectifier diodes
- R2: 510Ω, 1/4W color-coded resistor
- LEDs: 38 high-brightness white LED “straw hat†type
**Production Process**
1. Before starting, all components should be tested with a multimeter to ensure they are functional. Damaged parts can cause circuit failures, especially LEDs, since they are connected in series. If one is faulty, the entire circuit will fail. To test an LED, use the multimeter in the ×10k range, similar to testing a regular diode. Do not use other ranges.
2. Solder the DC drive circuit board. Components like diodes and resistors should be placed horizontally, while capacitors should be installed vertically.
3. Solder the LED board. The arrangement of LEDs is shown in Figure 3.
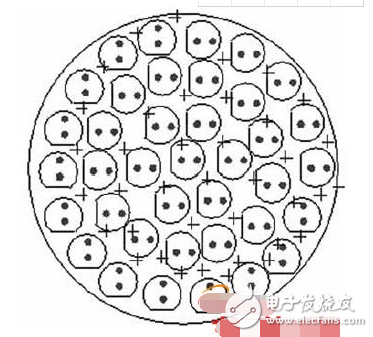
*Figure 3*
The LEDs should be neatly arranged, with correct polarity. The longer leg is the positive terminal, and the shorter one is the negative. You can align the LED with the notch and solder it with a suitable iron, then trim the excess leads with diagonal pliers.
4. Solder the AC power leads (marked with AC) and the LED power leads (marked with + and -).
5. Attach the DC drive circuit board to the lamp housing using hot melt glue, insert the LED board into the slot, and secure the back cover.
This step-by-step guide provides a clear understanding of how to assemble an LED energy-saving lamp efficiently and safely.