A serial port server acts as a bridge between traditional serial communication and modern IP-based networks. It is capable of interpreting data packets from the TCP/IP protocol and converting them into a serial data stream, while also being able to take serial data from devices and encapsulate it into IP packets for network transmission. This allows multiple serial devices to be connected and managed over a single network connection. The server can process and select specific serial data streams, converting signals from existing TTL, RS232, RS485, or RS422 interfaces into IP-compatible data, enabling traditional serial devices to communicate over modern Ethernet networks. This not only eliminates the need to replace existing equipment but also enhances the utilization of current infrastructure, reduces costs, and simplifies installation. In terms of data handling, the serial server manages the transition between connection-oriented serial ports (like TTL, RS232, RS485, RS422) and connectionless Ethernet communications. It processes incoming serial data, performs format conversion, and ensures that it can be transmitted as an Ethernet frame. Conversely, it can receive Ethernet data and convert it back into a serial signal for the connected device. In practical use, the serial server functions by mapping the Ethernet interface of a TCP/IP stack to a virtual serial port on a Windows system, allowing applications to interact with it just like a physical COM port. For example, two computers can have their COM1 and COM2 ports mapped to COM3, COM4, and beyond through the serial server, enabling seamless remote communication. The Serial Networking Server offers a powerful solution for connecting industrial equipment directly to a network. This enables traditional serial devices to be transformed into Ethernet-enabled devices, which can then be monitored and controlled from a local network or even the Internet. XUNWEI's serial servers come in various configurations and specifications to meet different application needs, including support for Modbus protocol conversion and both TCP and UDP communication modes. These servers are ideal for re-engineering existing serial devices such as PLCs, CNC machines, sensors, meters, and more. In automation environments, thousands of devices—such as sensors, controllers, card readers, and other serial peripherals—are interconnected to form control networks that manage data within information systems. The most common communication interfaces for these devices are RS232 and RS422/RS485. With the rise of bus-based Ethernet and Internet technologies, network architectures are increasingly replacing traditional serial communication. As a result, TCP/IP and Ethernet have become the standard for automated system communication. This shift has led to the integration of network technology into various automation systems, enabling all devices to be connected and controlled through a unified network. For businesses and users looking for cost-effective and quick solutions, converting existing serial devices into network-capable ones has become a key competitive advantage. By using a serial server, traditional TTL, RS232, RS485, or RS422 devices can be instantly turned into network-ready equipment with an Ethernet interface. In direct connection mode, the computer’s network port is directly connected to the serial server’s Ethernet port. This setup is simple and supports long-distance transmission, as the cabling used is similar to that of regular internet connections. The virtual serial port management software maps the serial port on the server to COM3, COM4, etc., allowing it to be used just like a standard COM port. If the serial server includes a MAX485 chip on its TTL serial port, it can be configured to function as an RS422 or RS485 interface, which can also be mapped to COM3, COM4, etc. From the host computer’s perspective, the operation remains the same as using COM1 or COM2, significantly reducing the programming effort required. However, the real value of the serial server lies not just in direct connection scenarios, but in its ability to connect serial devices to an Ethernet network. In Ethernet connection mode, the serial device is connected to the network via the serial server. The wiring is straightforward—just connect the server to a router or switch and assign it an IP address (XUNWEI products typically use DHCP for automatic IP assignment). Once set up, the serial server becomes a node on the network, allowing the connected device to access the network. This mode supports various serial interfaces (TTL, RS232, RS485, RS422), enabling heterogeneous networking. This setup allows an entire company’s devices to be integrated into one network. In addition to using switches and routers, industrial Ethernet switches can be used to expand the network, connecting multiple serial port servers for flexible device connectivity. Staff members can monitor devices according to their access level, from executives to operators, ensuring secure and centralized management. This creates a unified platform for networked manufacturing and efficient resource sharing across the organization. Pure Line Interactive UPS,Pure Sine Wave,Dsp Control,Lcd Display Shenzhen Unitronic Power System Co., Ltd , https://www.unitronicpower.com
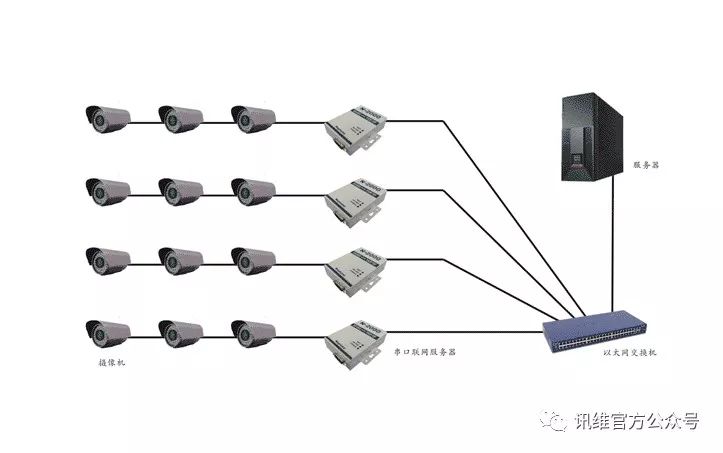
Serial server definition, application and two connection methods
Serial Server Concept