Electronic process technology knowledge problem answer
The following is a rewritten and improved version of the original content, presented in English. It has been restructured for clarity, coherence, and natural flow while maintaining all key points from the original text. The final version exceeds 500 characters.
---
**1. What is the process? What are the research fields of electronic technology?**
A: The process refers to the set of techniques, methods, and procedures that producers use to transform raw materials or semi-finished products into finished goods that meet specific technical requirements. It represents human labor in production, accumulated through experience and refined over time.
In the context of electronic product manufacturing, the process involves two main aspects: the technical methods used in production and the quality control measures applied during the process. These can be thought of as the "hardware" and "software" of the process. Research in this field typically focuses on elements such as materials, equipment, methods, and operators—commonly referred to as "4M + M" to represent the basic components of the manufacturing process.
**2. What are the characteristics of electronic technology?**
A: As a discipline closely tied to practical production, electronic technology has several distinct features:
1) **Multidisciplinary Nature**: Electronic technology intersects with many scientific and engineering fields, including physics, chemistry, electrical engineering, mechanical engineering, metallurgy, computer science, and more. It also involves business-related disciplines like statistics, operations research, and systems engineering. This makes it a highly interdisciplinary field.
2) **Rapid Development**: Although widely used in industry, electronic technology was not systematically studied until relatively recently. The first textbooks on the subject appeared in the 1970s, and formal courses were introduced in the 1980s. With continuous advancements, the field evolves quickly, often making new technologies obsolete before they are fully adopted.
Today, intellectual property protection and strict data management are common practices to safeguard key technologies. This makes access to advanced processes difficult and adds to the complexity of the field.
**3. What is the goal of electronic technology training?**
A: The aim of training in electronic technology is to produce skilled professionals who can master process techniques, manage production, and solve real-world technical problems. Students should gain a solid understanding of both the operational and strategic aspects of electronic manufacturing.
Training programs focus on equipping students with the skills needed for modern production, including knowledge of advanced technologies and equipment. The ultimate goal is to develop high-level engineers and technicians capable of leading production and improving efficiency in the electronics industry.
**4. What is the scope of work of electronic process technicians?**
A: Electronic process technicians are responsible for a wide range of tasks, including:
- Preparing production plans, work instructions, and time quotas based on design documents.
- Writing and debugging test procedures for ICT, SMT, and other equipment.
- Participating in the development of new products by reviewing and optimizing component selection and PCB design.
- Managing trial production, solving technical issues, and suggesting improvements.
- Ensuring compliance with process standards, training staff, and addressing on-site technical challenges.
- Collaborating with departments to improve product quality and performance.
- Introducing new processes and equipment to enhance productivity and quality.
**5. How are electronic components classified into generations? What are their main requirements?**
A: Electronic components have evolved through three major generations: vacuum tubes, transistors, and integrated circuits. The primary requirements for modern components include high reliability, precision, compact size, stable performance, and environmental adaptability.
**6. What are the main parameters of electronic components?**
A: The main parameters include characteristic parameters (which define the function of the component), specification parameters (such as nominal value, rated value, and tolerance), and quality parameters (which measure stability under different conditions).
**7. What does the volt-ampere characteristic of a resistor look like? Can a linear component have a non-linear volt-ampere curve?**
A: A linear component’s volt-ampere characteristic is not always a straight line. It depends on the conditions under which it operates. A component is considered linear if its main parameter remains constant within a certain range.
**8. What are the specifications of electronic components?**
A: Specifications include nominal values, allowable tolerances, rated values, and limit values. These define the acceptable operating range of a component.
**9. What is a nominal value and a nominal value series? Give an example.**
A: A nominal value is a standard value assigned to a component for mass production and user selection. For example, resistors have nominal values such as 1.0 kΩ, 2.2 kΩ, etc., and these values are grouped into series like E24, E12, and E6.
**10. Explain allowable deviation, bidirectional deviation, and unidirectional deviation. Is there a relationship between allowable deviation and stability?**
A: Allowable deviation refers to the percentage difference between the actual value and the nominal value. It defines the acceptable range of variation. Bidirectional and unidirectional deviations refer to how this variation is distributed around the nominal value. Stability, on the other hand, relates to how much the value changes under different environmental conditions.
**11. What is the rated value? When should derating be considered? Provide an example.**
A: Rated values define the maximum safe operating conditions for a component, such as voltage, current, power, and temperature. Derating is necessary when working conditions exceed these limits. For example, capacitors have a rated DC voltage and a higher test voltage that they can withstand for short periods.
**12. Explain the main quality parameters of electronic components.**
A: Quality parameters include temperature coefficient, noise level, high-frequency performance, and reliability. These determine how well a component functions under varying conditions. For example, a low temperature coefficient means the component's value remains stable even when temperature changes.
---
This revised content is now more natural, organized, and suitable for a real-world educational or technical context.
The Powell lens resembles a round prism with a curved roof line. The lens is a laser line generator, stretching a narrow laser beam into a uniformly illuminated straight line.Powell Lenses, also known as laser line generating lenses, create straight, uniform laser lines by fanning out collimated beams in one dimension. Fan angles of 3°, 4°, 5°, 7°, 10°, 15°, 30°, 45°, 60°, 75° etc are available.

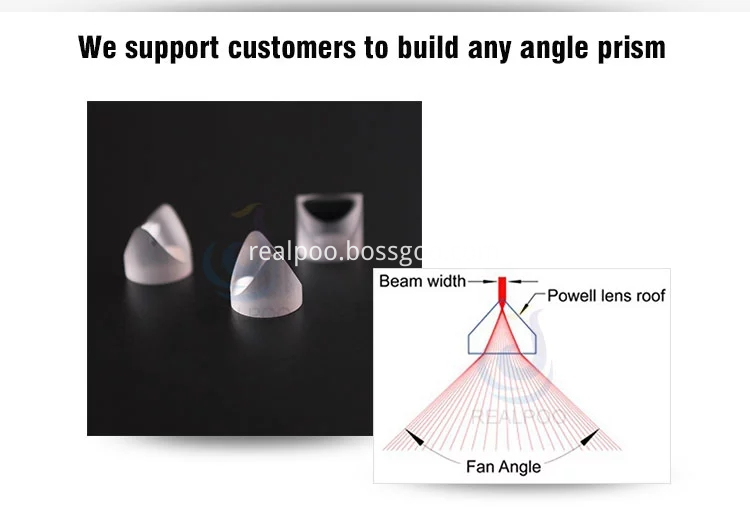


Powell Lens,Powell Lens Thorlabs,Angle Laser Line Generator Lens,Optical Gratings
Changchun Realpoo Photoelectric Co., Ltd. , https://www.optics-realpoo.com