In the new domestic car sales in Japan in 2009, Toyota's "Prius" topped the list with more than 200,000 vehicles. Now EV" title="HEV">HEV has become a popular car. HEV makes full use of the motor. It has improved the shortcomings such as energy consumption and exhaust emission during engine starting and deceleration, and also solved the problems of driving distance and charging time of EV. This paper introduces the types and characteristics of HEV system. This article refers to the address: http:// The battery that drives the motor uses a 288V Ni-MH rechargeable battery, and the remaining capacity during driving is calculated at any time by monitoring the charge and discharge status with the battery ECU and the EV·ECU. When charging the battery, use the car charger to communicate with the AC 200V commercial power supply. Hereinafter, the high-voltage rechargeable battery that drives the travel motor is referred to as a main battery, and the auxiliary drive rechargeable battery is referred to as a 12V battery. Fig. 2: The EV travel control determines the vehicle drive torque based on the accelerator opening and the brake signal. Summary of hybrid systems The characteristics of the tandem HEV are as follows. • Converting all engine power into electricity, so energy efficiency is slightly lower. · Drive control and power output control are simple. • The engine is running in a steady state, so it is easier to purify the exhaust. Parallel HEVs are equipped with an engine and a motor in parallel, and the driving power can be supplied by both parties (Fig. 5). In addition to the practical use of Honda as "IMA (Intelligent Motor Assist)", it has also been adopted by Daimler "Mercedes-Benz S400 HYBRID" and BMW "ActiveHybrid 7". In Honda's IMA, the engine and motor are connected in a direct connection and rotated at the same time. In contrast, many manufacturers have developed a system in which a clutch is interposed between an engine and a motor, and an EV is driven by disconnecting the clutch. The characteristics of the parallel HEV (Direct Connection) are as follows. • The power output of the motor only serves as an aid. The EV is hardly driven, so the motor is a small product. ·The motor has the function of a generator, so the regenerative power can only be used for driving after being stored in the battery. • EV running is possible by sandwiching the clutch between the engine and the motor, but a large power transmission motor is required. The MG here refers to an abbreviation of a motor and a generator. Since it is necessary to frequently switch between the motor function and the generator function, a portion originally called a motor or a generator is referred to as an MG. · The system efficiency is high, so the fuel efficiency improvement effect is remarkable. · System and control are more complicated.
The Outdoor Sports Light make some people feel loose while running, please be not mind before you buy
Bright and attractive Outdoor Sports Light, looks great on your shoes,or your wrist
Also can be clipped on your waist, mountain bicycle, etc
Light weight for carring when you go out for sport.
Outdoor Sports Light Led Shoe Lights,Arm Lamp,Outdoor Sports Light,Outdoor Flood Lights Ningbo Henglang Import & Export Co.,Ltd , https://www.odistarflashlight.com
The Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV) system is a perfect blend of engine and electric vehicle (EV) technology, making full use of the motor and battery technology used in EV. Although the EV has emerged since the dawn of the car and reached a practical level before 1900, it has not been fully popularized so far.
In the period of gasoline shortage after the Second World War, EV began to be listed in Japan as an alternative energy vehicle. In 1949, Japan's domestic EV production reached 3,299 units, accounting for 3% of Japan's car ownership at that time. However, with the improvement of engine vehicles and the popularity of gas stations, the momentum of EV began to decline in Japan.
Since then, the automotive industry has been developing EVs for environmentally friendly vehicles since 1971. At that time, the Industrial Technology Institute of the Ministry of International Trade and Industry of Japan started the research and development of EVs using a large-scale project system (involved by automobile, motor and battery manufacturers), and many automobile manufacturers and component manufacturers invested a lot of energy. However, after 1980, with the advancement of engine exhaust purification technology, EV disappeared again.
In 1990, 20 years later, the State of California of the United States enacted the exhaust emission regulations "ZEV Act" (Zero Emission Vehicles Act). At that time, no car other than EV was able to meet this requirement, so the development of EV was once again started.
The implementation of the ZEV Act was in 1998, and companies were struggling to develop because they had to sell a specified percentage of EVs. However, the regulation was not implemented on schedule and ended up in a limited number of years of production.
HEV using EV element technology
As described above, the EV has problems in terms of travel distance, charging time, and cost, and has been widely used only in specific use fields such as forklifts.
The vehicle that solves the above-mentioned problems of the EV, which is superior in fuel efficiency to the engine car and achieves low emissions, is the HEV that was introduced in the second half of 1990. Toyota launched the "Prius" in 1997, and Honda launched "Insight" in 1999.
These HEVs use EV element technology developed to comply with the ZEV Act. In particular, nickel-metal hydride rechargeable batteries have been adopted in the Toyota "RAV4EV" and Honda "EV PLUS" which were put into practical use in 1996. Since it helps to extend the EV's continuous driving distance, it is not unreasonable to say that the HEV does not have a Ni-MH rechargeable battery. In addition, not only a battery, but also a permanent magnet (PM) synchronous motor using a rare earth magnet developed for EV has contributed to the improvement of HEV performance.
Before introducing the HEV system, let's talk about the EV developed to comply with the ZEV Act. Figure 1 shows the system configuration of the Toyota RAV4 EV. This system controls the inverter by the EV·ECU (Electronic Control Unit) to drive the travel motor based on the amount of depression detected by the throttle sensor. The motor uses a permanent magnet motor. 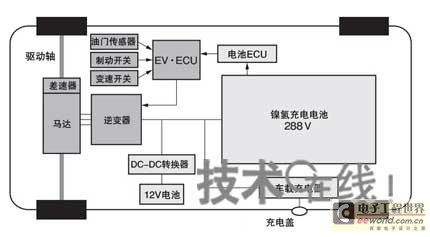
Figure 1: System structure of Toyota "RAV4 ​​EV"
A practical EV equipped with a nickel-metal hydride rechargeable battery in 1996.
In the EV running control, the required driving torque is determined by the driving torque map based on information such as the accelerator opening degree, the brake signal, the gear position, and the vehicle speed. The vehicle control unit of the EV·ECU issues a torque command to the motor control unit, and transmits a command to the inverter via a PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) signal. Motor control is used as a motor when accelerating or normal running, and as a generator when decelerating (Figure 2). 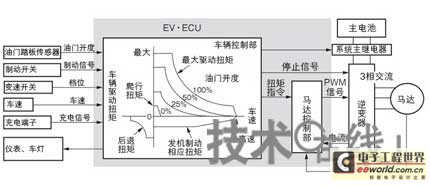
There are two classification methods for hybrid systems. One is classified according to the achievable functions, and the other is classified by means of a drive mechanism.
First, sort by function, as shown in Figure 3. Only the non-idle function is called the micro HEV or ISS (Idling Stop System). Adding acceleration assistance, energy regeneration, and engine efficient operation functions to this function is called weak HEV, and if the EV driving function is added, it is called strong HEV. The closer to a strong HEV, the less CO 2 emissions and tail gas. The EV emissions are all zero. Further, a plug-in type HEV (PHEV) and a range extender type EV that extends the travel distance by operating the power generation engine are positioned between the strong HEV and the EV. 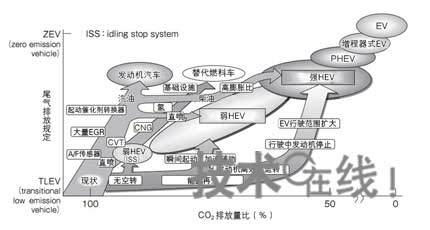
Figure 3: CO2 reduction effects of HEV and EV
Hybrid systems are classified according to different functions.
(1) Tandem HEV
The tandem HEV is equipped with an engine and a generator that charges the main battery, and is driven by a motor while charging (Fig. 4). It can also be considered that the engine and the generator are added to the EV. In commercial vehicles, this method is used more frequently on buses than in private passenger cars. Toyota’s “Coaster HEVâ€, which was launched in 1997, and “Aero Nostep HEVâ€, which was launched in 2004 by Mitsubishi Fusokar Bus, were adopted. The way. 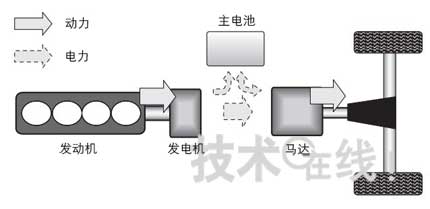
Figure 4: Composition of a series HEV
Drive by motor only. Equipped with high power large motors.
·The motor is driven only by the motor, so the motor and generator are high-power large products compared with other methods.
(2) Parallel HEV 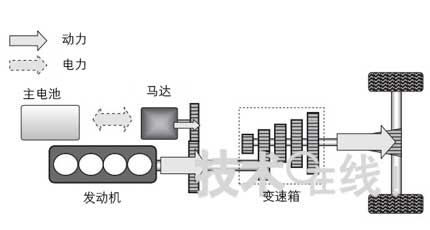
Figure 5: Composition of a parallel HEV (direct connection)
The motor only serves as an auxiliary and uses a small product.
- It is easy to add a motor between the engine and the transmission of the conventional model.
(3) Series-parallel HEV
A representative example of the series-parallel HEV is "THSII (Toyota Hybrid System II)" adopted by Toyota Prius. In this manner, the three types of power sources of the engine, MG1, and MG2 are integrated by the planetary gear mechanism, and these power sources are combined according to the traveling state to be driven (FIG. 6). 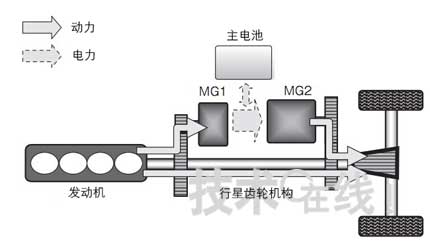
Figure 6: Composition of a series-parallel HEV
At the same time, it has the advantages of both series mode and parallel mode.
The role of the engine is to drive the vehicle and drive the MG1. In addition to charging the main battery, the MG1 also includes starting the engine as a motor and driving assistance to the vehicle. The role of MG2 is to achieve EV driving, acceleration assistance, and energy regeneration as a generator.
The characteristics of the series-parallel HEV are as follows.
· It has the advantages of both series mode and parallel mode, taking into account fuel efficiency and driving performance.
Analysis of Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV) System and Control Method
When classifying by driving method, it is mainly divided into three types: tandem HEV, parallel HEV, and series-parallel HEV. Let's take a look at the composition and characteristics of the three.