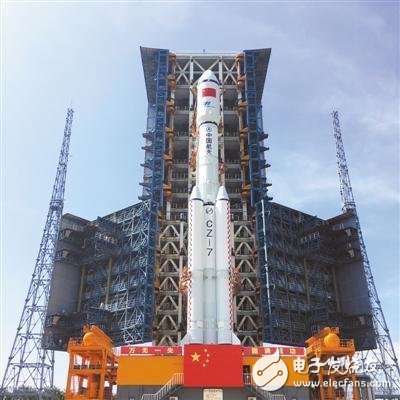
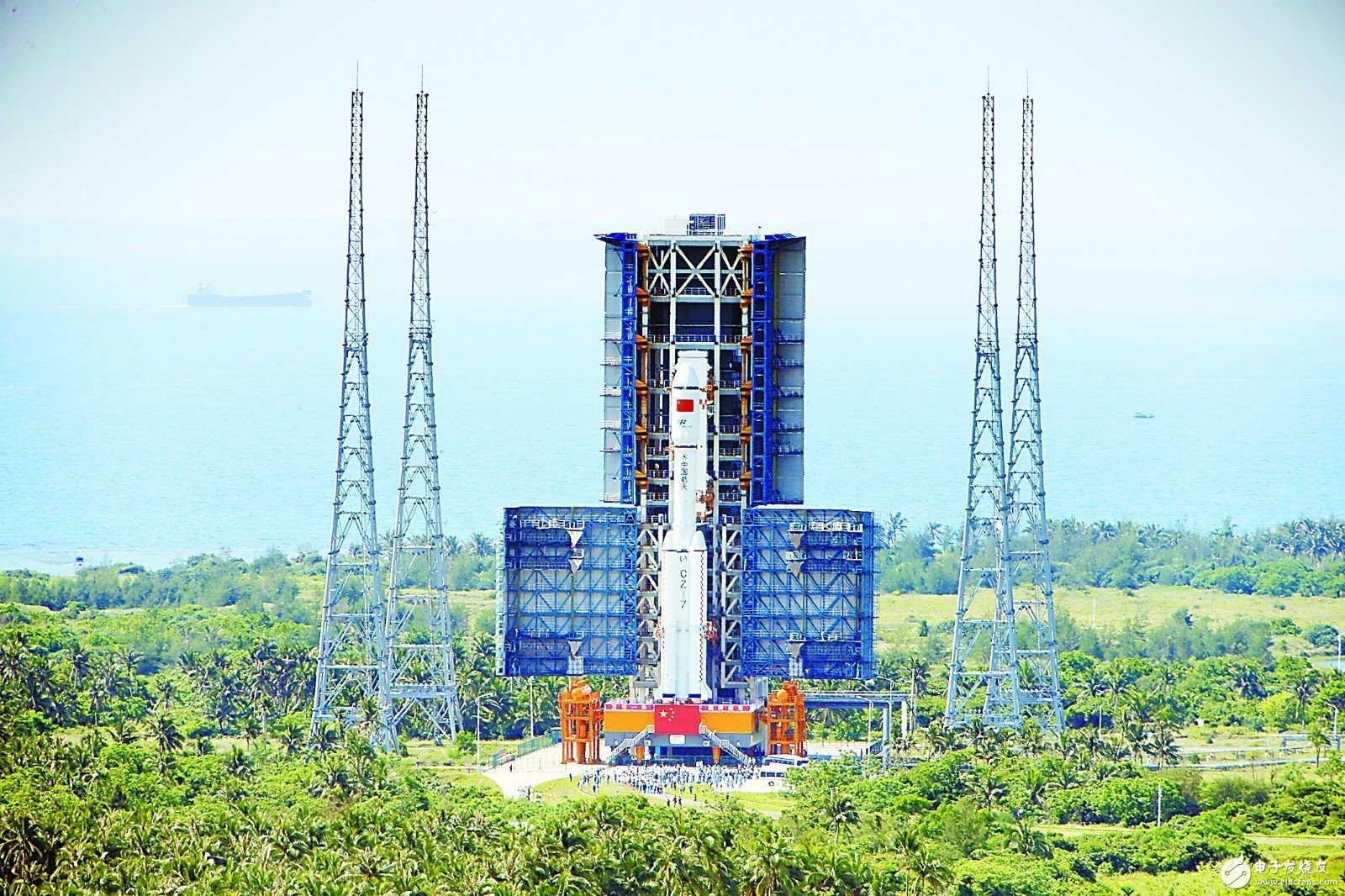
According to CCTV News reported on April 19, the Tianzhou No. 1 launch mission yesterday (18th) carried out the last joint training of the whole district. The results showed that the system organization and command were smooth, the technical status was correct, and the test equipment was in good condition. This joint training was organized and implemented by the Wenchang Space Launch Site. It is the most comprehensive, most comprehensive and close-to-actual comprehensive simulation exercise in addition to the “Ignition Launchâ€. It is also the last joint training before launch. At present, the five systems of launching, measuring, control, communication, meteorology and diligence are simultaneously launched. According to the plan, the Tianzhou-1 cargo spacecraft will be launched from the 20th to the 24th of this month. From the results of the meteorological meeting, the weather conditions of the launch window will meet the launch requirements. The launch is a zero-window launch and faces great challenges. Zhang Xueyu, commander of the launching section of the Tianzhou-1 mission, said: Zero-window launch is the first time in Wenchangchang. It is mainly because the cargo ship must be accurately docked with Tiangong-2 after it is in orbit. It is necessary to coordinate and cooperate with each system. Precise control and precise decision-making ensure that the spacecraft can successfully and successfully enter the track on time. At present, the status and parameters of each equipment are normal and have launch conditions. What is a "zero window" launch? The launch window refers to a time range in which the launch vehicle carries a spacecraft to launch a space, some in hours, and some in days, during which the rocket can be launched. Because the launch of the Tianzhou-1 spacecraft and the Tiangong-2 space laboratory to achieve rendezvous and docking, the launch accuracy is very high, therefore, the launch window is not a time range, but a certain point in time, one second can not be bad This is what the astronauts call "zero window", which puts high demands on the reliability of the rocket and launch site systems. Wang Xiaojun, chief commander of the Long March 7 carrier rocket of the Aerospace Science and Technology Group, said that because of the "zero window" launch, the rocket composition requires a complex system. In addition, the operation and flow before shooting are also very complicated. In any part of the working process, there is a problem, we will have certain difficulties in ensuring zero window launch. In addition to the rocket itself, the rainy weather in Hainan has also become an important factor affecting the rocket's on-time departure. At the beginning of the development of the Long March 7th, the designer added the ability of “rain and waterproofâ€, making it the first launch vehicle in China that can be launched under moderate rain conditions, ensuring that it can also be used in inclement weather. The ability to achieve zero window emission. In addition to the Hainan Wenchang Launch Center, the launch sites currently in use in China are basically located in the central and western regions of China, dry and less rainy. Since the Long March 7 rocket was launched in Wenchang, Hainan, the humid and rainy climate and the low-temperature fuel inside the rocket made the demand for “waterproof†appear for the first time in the development of the Chinese launch vehicle. "Space Express Brother" is preparing for the first flight According to the China Manned Space Engineering Office, the Tianzhou-1 cargo spacecraft and the Changzheng No. 7 remote two carrier rocket completed the technical work of the final assembly test and other technical areas on April 17. At 7:30 on the same day, the activity launching platform carrying the combination of the Long March 7 remote two launch vehicle and the Tianzhou-1 cargo spacecraft sailed out of the assembly test building, and after a smooth running for about 2.5 hours, it was transported vertically to the launch area. After that, the function check and joint test of the Tianzhou-1 cargo spacecraft and the Long March 7 remote launch vehicle will be carried out in the launch area. After the final status confirmation is completed, the rocket will be filled with propellant and plan to launch the aircraft from April 20 to 24. . Tianzhou No.1 is the first cargo spacecraft independently developed by China. Because it only transports goods and does not give people, it has been nicknamed “Courier Brother†by some media. It has a two-cabin structure, the smaller diameter is the propulsion cabin, and the larger diameter is the cargo compartment. Its maximum diameter reaches 3.35 meters, the spacecraft has a total length of 10.6 meters, the load capacity reaches 6.5 tons, and it weighs 13.5 tons when loaded with cargo. If it is fully loaded, it is likely to become the mass-quality payload that China launches into space. Even larger than the Tiangong-2 Space Laboratory, the latter has a total length of 10.4 meters, a diameter of 3.35 meters and a mass of 8.6 tons. China’s first “space refueling†is eye-catching It is understood that Tianzhou No. 1 adopts a two-cabin configuration and consists of a cargo compartment and a propulsion compartment. One of the core missions of the Tianzhou-1 is to verify the propellant on-track supplementation technology, which is also known as the "space refueling" technology. In order to maintain its orbital height, the space station must consume fuel during the flight. In order to make the space station use for a long time, it is necessary for the cargo spacecraft to replenish the space station. Tianzhou No. 1 will add fuel to Tiangong No. 2 through some unique interfaces to create a new chapter in China's space. Experts said that whether it is a space laboratory or a space station, the operation in low earth orbit will "fall off the height" due to air resistance. If the altitude cannot be maintained, its on-orbit life will be limited. This requires the rocket engine to start at the right time to maintain the track height, but the fuel it carries is limited. This raises the need for in-orbit propellant supplementation technology known as "space refueling." At present, only the United States and Russia are in charge of the propellant on-track supplement technology. An important mission of the Tianzhou-1 is to verify this technology. This is also one of the key technologies that determine the smooth development of China's future space station. To this end, Tiangong No. 2, which was first launched into the orbit, installed a new supplementary system. The supplementary principle is similar to the docking of the oil pipe and the oil gun, but the accuracy and sealing requirements are very high. Experts said that there is still a way to maintain the track in the international arena. After the cargo spacecraft docks with the space station, it uses its own engine to “burn off†excess fuel to raise the orbit of the space station. However, this track maintenance method has high requirements for the position of the spacecraft and the force on the interface, and this method is also not flexible enough. According to estimates by McDonnell Detwell, Canada, between 2012 and 2020, more than 100 geosynchronous orbit communication satellites may fail due to fuel exhaustion, and the cost of replacing these satellites is as high as $30 billion to $36 billion. If the on-orbit spacecraft can be used to refuel these on-orbit spacecraft and extend their service life, the launch cost can be effectively reduced. "Space refueling" will be a landmark milestone for China Aerospace following the mastery of space rendezvous and docking technology. It will enable the construction of a long-term, manned space station with basic premise, laying the foundation for the establishment of a "space home" after 2020 and the birth of the Chinese space station era. The strongest cargo ship with the best carrying capacity Experts said that China plans to build a space station around 2022. Its initial scale includes a core cabin and two experimental cabins. If you want to keep the astronauts in orbit for a long time, the cargo spacecraft is bound to be a lot. Experts said that the cargo spacecraft evolved from a manned spacecraft. The cargo spacecraft can transport propellant fuel, repair and replacement equipment, astronauts' lives, work supplies, and space science laboratory equipment and supplies, as well as adjust the space station's orbital height. In the 1970s, the former Soviet Union and the United States began to develop space stations that were large, long-lived, and versatile. At the beginning, both countries used a manned spacecraft mixed with people to provide a small amount of replenishment for the space station. Each manned spacecraft could only transport hundreds of kilograms of material to the space station at one time, which could not meet the demand. The Soviet Union pioneered the development of the Progressive Cargo Spacecraft on the basis of the Soyuz manned spacecraft, with a cargo hold of 6.6 cubic meters, a carrying capacity of 2.6 tons, and an on-orbit propellant supplement service. The European cargo ship is called an automatic transfer aircraft. It has a total length of 10 meters, a maximum diameter of 4.5 meters, a weight of about 10 tons, and a cargo capacity of 7 tons. It is the largest cargo ship with the capacity to date, from 2008 to 2014. Five were launched, but construction has stopped. The US "Dragon" spacecraft is 5.9 meters long and has a maximum diameter of 3.7 meters. Its maximum payload capacity is 6 tons, and the maximum return mass is 3 tons. It is also the master of cargo ships returning goods to the earth. In addition, the US "Cygnus" and Japan's HTV cargo spacecraft carrying capacity of 2.7 tons and 6 tons respectively. In general, the carrying capacity of the Tianzhou-1 is at the forefront, and its carrying capacity is the largest in active cargo ships. Guangdong Ojun Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.ojunconnector.com